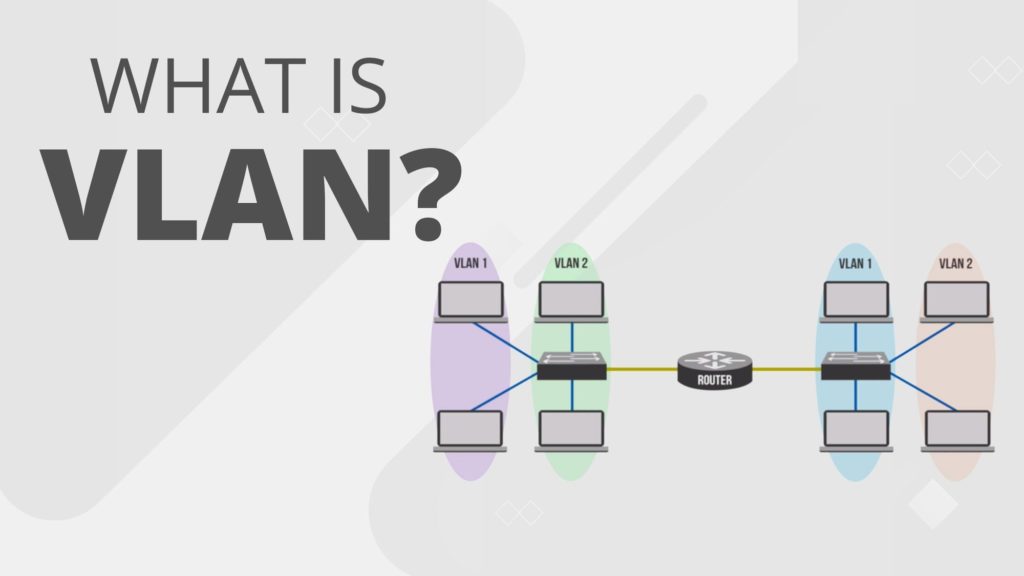

Welcome to the world of networking, where data flows freely and connections are made every second. In this digital era, it’s crucial to have a robust and efficient network infrastructure that can handle the ever-increasing demands of our connected lives. And that’s where VLANs come into play.
You may have heard the term “VLAN” thrown around in IT circles or seen it mentioned in networking discussions, but what exactly is a VLAN? How does it work? And why should you even care about it?
Well, my curious friend, you’re in luck! In this blog post, we’ll demystify the concept of VLANs and explore their many benefits for your network setup. So buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the exciting world of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)!
Ready? Let’s go!
Benefits of Using VLANs
One of the major benefits of using VLANs is improved network security. By segmenting your network into different virtual LANs, you can control access and traffic flow between devices. This helps to reduce the risk of unauthorized users gaining access to sensitive data or compromising your network.
Another advantage is enhanced network performance. With VLANs, you can prioritize certain types of traffic, such as voice or video data, over others. This ensures that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth and reduces congestion on the network.
VLANs also offer increased flexibility and scalability. As your organization grows or changes its requirements, you can easily reconfigure VLAN settings without physically rearranging devices or rewiring them. This makes it more cost-effective and efficient to adapt your network infrastructure as needed.
Furthermore, VLANs enable simplified management and troubleshooting. By grouping devices based on their function or location into separate virtual networks, it becomes easier to monitor and manage each VLAN independently. This streamlines administrative tasks and simplifies problem isolation when issues arise.
In addition, implementing VLANs can lead to reduced hardware costs by eliminating the need for multiple physical switches in a single location. One switch can be used to create multiple logical networks through encapsulation techniques like IEEE 802.1Q tagging.
Utilizing VLAN technology brings numerous advantages including improved security measures, optimized performance allocation, flexible scalability options,and simplified management processes
Types of VLANs
1. Port-based VLANs: This is the most common type of VLAN, where ports on a switch are assigned to specific VLANs based on their physical location. Each port can only be a member of one VLAN at a time.
2. MAC address-based VLANs: In this type, devices are assigned to different VLANs based on their MAC addresses. This allows for more granular control over network access, as devices with certain MAC addresses can be restricted to specific VLANs.
3. Protocol-based VLANs: With protocol-based VLANs, traffic is segmented based on the protocols used in communication. For example, all VoIP traffic could be placed in one VLAN while data traffic remains in another.
4. Dynamic (or membership) VLANS: These types of VLANS allow for dynamic assignment of ports to different VLANS based on factors such as user authentication or device characteristics.
5. Community and private VLANS: Community VLANS group together multiple independent VLANS that share common requirements or security policies, while private VLANS isolate individual ports within a single subnet from each other.
Remember that these are just some examples; there may be additional types and variations depending on your specific network requirements!
How to Set Up a VLAN
Setting up a VLAN may seem like a complex task, but with the right steps, it can be done smoothly. Here’s how to set up a VLAN in just a few simple steps.
You need to determine your network requirements and plan accordingly. Identify which devices or groups of devices need to be isolated from each other and categorize them into different VLANs.
Next, you’ll need to configure your network switch. Access the switch’s management interface and navigate to the VLAN configuration section. Create the necessary VLANs by assigning them unique IDs and names.
After creating the VLANs, assign ports on the switch to their respective VLANs. This will ensure that devices connected to those ports are part of the designated VLAN.
To enable communication between different VLANs or subnets, you’ll need a layer 3 device such as a router or layer 3 switch. Configure inter-VLAN routing by setting up IP addresses for each virtual interface corresponding to each VLAN.
Test your setup by connecting devices within each VLAN and ensuring they can communicate with one another while remaining isolated from other networks.
Remember that these steps may vary depending on your specific networking equipment and software interfaces used. It is always recommended to consult product documentation or seek professional assistance if needed.
Common Uses for VLANs
VLANs, or Virtual Local Area Networks, have become an indispensable tool in modern networking. They offer a multitude of benefits that can greatly enhance the efficiency and security of network infrastructure. But what are some common uses for VLANs?
One common use is to segment different departments within an organization. By dividing the network into separate VLANs, each department can have its own virtual network space, enabling better control over access and resources. This not only improves security but also simplifies network management.
Another popular application is in guest networks. With a VLAN dedicated to guest users, organizations can provide internet access without compromising their main internal network’s privacy or performance. This separation ensures that guests remain isolated from sensitive data while still enjoying connectivity.
In larger environments such as universities or hotels, VLANs are often used to segregate traffic between different user groups like students, faculty members, and guests. By creating distinct VLANs for each group, administrators can manage bandwidth allocation more effectively and ensure fair usage policies.
Furthermore, Voice over IP (VoIP) systems commonly utilize VLAN technology to prioritize voice traffic on the network. This ensures high call quality by guaranteeing sufficient bandwidth for VoIP calls and reducing any potential interference from other data-heavy applications.
Additionally, multicast services like video streaming or IPTV benefit greatly from the implementation of VLANs. By dedicating specific VLANs to multicast traffic delivery across the network infrastructure efficiently handles high-bandwidth content distribution without impacting other areas of the network.
These are just a few examples showcasing how versatile and essential VLAN technology has become in today’s networking landscape. Whether it’s improving security measures through segmentation or optimizing resource allocation for specific purposes like VoIP or multicast services – implementing VLANS offers countless advantages when it comes to managing complex networks.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
One common issue is VLAN misconfigurations. This can occur when a port is incorrectly assigned to the wrong VLAN or when there are overlapping IP address ranges within different VLANs. To troubleshoot this, administrators should carefully review the switch configurations and verify that each port is assigned to the correct VLAN.
Another potential problem is connectivity issues between different VLANs. If devices in one VLAN cannot communicate with devices in another, it could be due to a routing issue or an incorrect configuration on the router or Layer 3 switch. Troubleshooting involves checking the routing tables, ensuring proper inter-VLAN routing is configured. Also, verifying that access control lists (ACLs) are not blocking traffic between VLANs.
In some cases, performance problems may also occur within specific VLANs. This could be caused by excessive broadcast traffic or insufficient bandwidth allocation for certain applications or services. Administrators should monitor network traffic using tools like packet analyzers to identify any bottlenecks or abnormal behavior within individual VLANS.
Regular maintenance tasks for a VLAN network include monitoring device health, applying software updates for switches and routers, reviewing security policies regularly, and conducting periodic audits of ACL rules to ensure they align with current requirements.
By understanding these common troubleshooting challenges and implementing regular maintenance practices, administrators can effectively manage their VLAN networks and keep them running smoothly without compromising performance or security.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the world of VLANs and gained a better understanding of their importance in modern networking. VLANs provide numerous benefits, such as improved security, enhanced network performance, and simplified network management.
By segmenting a large network into smaller logical networks using VLANs, organizations can effectively control access to sensitive data and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. They also allow for more efficient use of bandwidth by limiting broadcast traffic to specific groups within the network.
Setting up a VLAN may require some initial configuration and planning, but no worries, with the right knowledge and equipment, it can be done seamlessly. Whether you are using a physical switch or virtualized switches in software-defined networking environments. Creating VLANs allows you to tailor your network infrastructure to meet your specific needs.
VLANs find application in various scenarios – from dividing departments within an organization to isolating guest networks in public Wi-Fi setups. They offer flexibility and scalability that traditional LAN configurations simply cannot match.
However, like any technology implementation, troubleshooting issues may arise when working with VLANs. It is important to have a solid understanding of how they function. This way any problems can be quickly identified and resolved.
To sum it up, VLANs are powerful tools that enable organizations to optimize their networks for better performance while enhancing security measures. It’s important to implement proper setup procedures along with routine maintenance practices. Businesses can reap the full benefits that VLAN technology has to offer.
So next time you hear about VLANS or come across them while setting up your own network infrastructure – remember that they are not just fancy acronyms! Instead,VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network: an essential component of modern networking systems designed for efficiency,simplicity,and enhanced security!