If you’re not in the business world, you might not be familiar with the term “intranet.” An intranet is a private network that’s internal to an organization. It can only be accessed by employees or other authorized users.
An intranet is different from an extranet, which is a private network that’s shared with external partners or customers.
While both intranets and extranets use similar technologies, they serve different purposes. Intranets are used to share information and resources among employees, while extranets are used to share information and resources with external partners or customers.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between intranets and extranets, and how each can be used to benefit your organization.
Table of contents
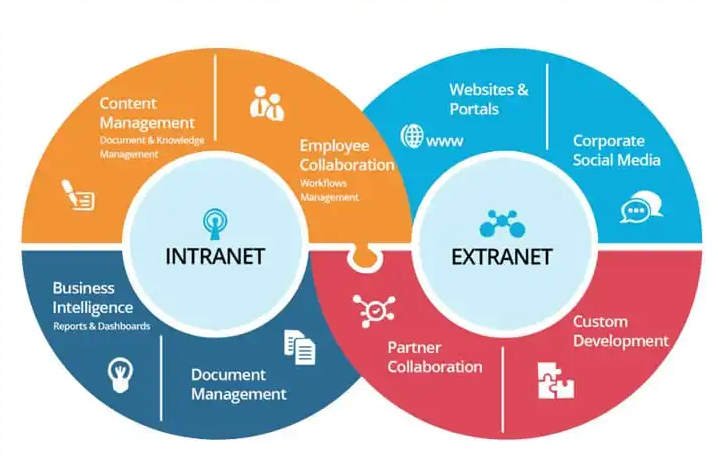
What is an Intranet?
An intranet is a computer network that uses Internet protocols and technologies to securely share information, data, and other resources within an organization. It can be used to facilitate communication between employees, partners, and customers. Intranets are typically accessible only to authorized users, such as employees of a company or members of an organization.
Extranets are similar to intranets, but they allow access to authorized users outside of the organization. Extranets can be used to share information with partners, suppliers, or customers.
Like intranets, extranets use Internet protocols and technologies to securely share information. However, because extranets allow access to users outside of the organization, they typically require additional security measures, such as authentication and authorization.
What is an Extranet?
An extranet is a network that allows access to part of a company’s internal network to authorized outside users. This usually includes partners, vendors, and suppliers who need to be able to access some of the company’s data or systems.
An extranet can be thought of as an extension of a company’s intranet that is accessible to outsiders. However, an extranet typically has much more limited access than an intranet and is usually only available to a select group of users.
The Difference Between an Intranet and Extranet
An intranet is an internal network that is designed for use only by a company’s employees. An extranet is an external network that allows companies to extend access to their internal network to specific outsiders, usually business partners or customers.
The main difference between an intranet and an extranet is who has access to the information contained within each network. An intranet is typically only accessible to employees of a company, while an extranet may be accessible to employees, business partners, and customers of a company.
The level of access that each group has to the information contained within the network can be controlled by the administrator of the network.
The security of an intranet is typically higher than that of an extranet because only authorized users have access to the information contained within the network. The security of an extranet depends on who has been given access to the system and what level of access they have been granted.
It is important to carefully consider security risks when setting up an extranet since it provides outsiders with access to a company’s internal network.
Pros and Cons of an Intranet
An intranet is a private network that is contained within an enterprise. It uses the same Internet protocol suite and architecture as the public Internet, but it is only accessible to authorized users within the enterprise.
An extranet is a private network that uses the public Internet infrastructure and protocols to securely connect authorized users outside of the enterprise.
The main difference between them is that an intranet is designed for use by internal employees. In contrast, an extranet is designed for use by external partners or customers.
There are several pros and cons to using an intranet:
PROS:
-Allows easy communication and collaboration between employees
-Can be used to store and share important company information
-Can be customized to fit the specific needs of the company
-Improves security by keeping confidential information within the company network
CONS:
-Requires investment in hardware and software
-May require IT staff to manage and maintain the system
-Not accessible to people outside of the company
How to Implement an Intranet
An intranet is a private network that is only accessible to employees of an organization. In order to implement an it, an organization must first set up a network infrastructure and then purchase or develop the necessary software applications. Once the infrastructure and applications are in place, employees can be given access to the intranet according to their needs.
One of the benefits of setting up an intranet is that it can help to improve communication within an organization. In many cases, employees are spread out across different locations and need a way to share information and collaborate on projects. An intranet can provide a central repository for documents, allow for real-time chat between employees, and even provide video conferencing capabilities.
Another benefit of an intranet is that it can help to improve productivity. By having all of the necessary information and tools available in one place, employees can spend less time searching for things and more time getting work done. In addition, applications on an intranet can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization, which can further improve productivity.
If you are considering implementing an intranet for your organization, there are a few things to keep in mind.
First, you will need to ensure that you have a robust network infrastructure in place.
Second, you will need to purchase or develop the necessary software applications.
Finally, you will need to decide how you will give employees access to the intranet according to their
Conclusion
An intranet is a private internal network for businesses or other organizations, while an extranet is part of that it that can be accessed by authorized outsiders. Intranets are usually much more secure than the public internet, but they can also be more expensive to set up and maintain.
Extranets extend the reach of an organization’s intranet beyond its walls, allowing authorized users outside the organization to access certain resources.
If you’re in need of that little extra you can always have a VPN enabled for maximum connection security and reliability.